Clippings, alpha masking, masking – What are the differences?
Clipping images and objects is probably one of the most common tasks in image processing and is indispensable in e-commerce, for example. In general, the aim is to detach the motif to be cut out from its original background during the editing process, usually to remove the background and to obtain a stand-alone object as a result – a clipping. This can then be placed, for example, on a new background, as in a composing.
But is clipping always the same? No, not at all! Because clippings can be created in different ways. Depending on the complexity of the images, quality requirements and subsequent intended use, a different method is used for clipping.
What’s what? When is which method used and why? We explain the differences between clipping, alpha masking and masking.
Clippings

What?
Typically, the term Clipping refers to an object or motif that has been separated using a single vector path. This vector path is called a “simple path”. If the simple path is defined as a clipping path, it also contains information about which image areas are to be exposed and which are to be hidden.
How?
There are various tools available to create clippings using a vector path. Which tool is suited best depends on the motif and the desired result. For example, Photoshop provides the following clipping tools: Marquee Tool, Magic Wand Tool, Lasso Tools, Quick Selection Tool, Pen Tool.
What for?
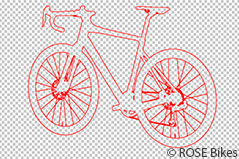
Motifs with clear and simple contours are ideal for clipping by vector path. This is often the case, for example, with product pictures or packshots. However, depending on the motif, the complexity of a clipping is different.
– Simple: few details on the edges, e.g. furniture, decorative items, fashion like flat lay
– Medium: more detailed, but still sharp contours, e.g. clothes, tools, flowers
– Difficult: many details with complex contours that require many individual path sections, e.g. bicycles, Christmas trees, jewellery
People can also be cut out using a vector path, provided the motifs do not have too fine details; which, however, is often the case, especially in the hair area. Then a different clipping method is used.
You can find more details about clippings here Clippings explained!
Alpha maskings

What?
Not every motif is suitable for clipping using a vector path. Due to the hard contours of the path, details are quickly lost in complex motifs with fine image elements.
Alpha maskings are used for a smooth transition at the edges and precise cropping of even the finest image details. Other terms are soft masking or alpha channel clipping.
How?
In case of alpha masking, the image motif is cropped by editing the individual colour channels and using the contrast to the background. There are several methods of creating alpha masks. The effort depends on various factors: the overall complexity of the image motif, the difference in contrast between the object and the background, etc. The editing process can be relatively quick or even take several hours.
For a better overview and more transparency, we therefore divide alpha maskings into levels 1 to 4; depending on the motif, effort and the desired result. This is also important for the later use of the results. Level 2 is usually sufficient for online use. While for print products of sufficient quality at least level 3 is necessary, for large items such as posters even level 4. The exact differences and more we have summed up here All you need to know about alpha maskings.
What for?
Complex motifs with fine image elements that would be lost if they were cut out via a path are cut out with alpha masks. These include, for example, hair, fur, textile structures, filigree leaves or motifs with semi-transparent or, even transparent areas such as smoke, bottles or fashion items such as wedding dresses.
Maskings

What?
In contrast to clippings and alpha maskings, which separate objects as a whole from the background with only one clipping path, maskings separate individual image elements from the background and from each other using separate paths. The image is, so to speak, “split up” into individual parts. These individual parts can then be displayed and adjusted individually, independently of another. Since the result contains more than one clipping path, they are also called multipath clippings.
How?
Maskings use various clipping methods in combination; depending on which method is best for an image area. Areas with clear contours are, for example, cut out with the path tool. While for blurred or very detailed areas alpha masks are used. Each image component can then be shown or hidden, edited or replaced individually.
What for?
Maskings offer maximum flexibility in design and editing. Almost every detail of a motif can be cut-out individually with an individual masking path. This makes masking particularly interesting for the representation of different product variants. Maskings are very often used as a preparation for colour corrections and recolouring. In this case we speak of colour masks. Instead of photographing and cutting out each product variant individually, the details to be changed are separated from each other by individual masking paths with just one initial image and then adjusted separately. During image retouching, specific corrections can be made with the help of masking. You can find even more information about maskings here What are maskings?
At a glance
| CLIPPING
|
ALPHA MASKING |
MASKING |
– Separation of the motif and background by a vector path – Motifs with clear, simple outlines – Depending on the motif: simple, medium, complex clippings – File formats: JPEG, TIF, PSD |
– Separation of the motif and background by editing individual colour channels – Motifs with fine picture elements, blurred edges, semi-transparent / transparent areas – Level 1-4 in processing – File formats: TIF, PSD |
– Separation of the motif and background as well as individual image components from one another by several separate masking paths – Combination of different clipping methods – E.g. to display different product variants, preparation for color corrections and recolouring – File formats: JPEG, TIF, PSD |
Looking for the best clippings in the highest quality? Look no further. We cut-out everything that you need.
Our services include: clipping, alpha masking, masking, composing, ghost model, image retouching, colour correction, layout design, CGI for e-commerce, and more.
For more information, samples and detailed prices download our e-commerce & product images portfolio.
- 2023
- January (1)
- 2022
- December (2)
- November (1)
- October (2)
- September (2)
- August (1)
- July (1)
- June (1)
- May (1)
- April (1)
- March (1)
- February (1)
- January (3)
- 2021
- December (2)
- November (1)
- October (3)
- September (2)
- August (1)
- July (3)
- June (1)
- May (2)
- April (1)
- March (1)
- February (2)
- January (4)
- 2020
- December (2)
- November (3)
- October (4)
- September (1)
- August (2)
- July (1)
- June (2)
- May (3)
- April (3)
- March (3)
- February (4)
- January (4)
- 2019
- December (1)
- November (2)
- October (5)
- September (1)
- August (3)
- July (2)
- June (2)
- May (3)
- April (2)
- March (3)
- February (2)
- January (4)
- 2018
- December (2)
- November (2)
- October (3)
- September (3)
- August (2)
- July (2)
- June (2)
- May (1)
- April (1)
- March (2)
- February (3)
- January (2)
- 2017
- December (2)
- November (2)
- October (1)
- September (1)
- August (1)
- July (1)
- June (1)
- May (1)
- April (1)
- March (1)
- February (1)