All about colour – Colour model, space, profile & gamut mapping
The following terms do not only appear in the area of image editing.
Colour model
Colour models describe colours with the help of mathematical formulas and geometric shapes and relate them to each other. As a result, the colour spectrum is visualised as a multi-dimensional model.
There are different colour models, best known are probably RGB and CMYK. The RGB colour model is based on the primary colours Red, Green and Blue. The CMYK colour model is based on the primary colours Cyan, Magenta and Yellow as well as the Key colour black. Other colour models, such as the HSL colour model, are based on Hue, Saturation and Lightness.
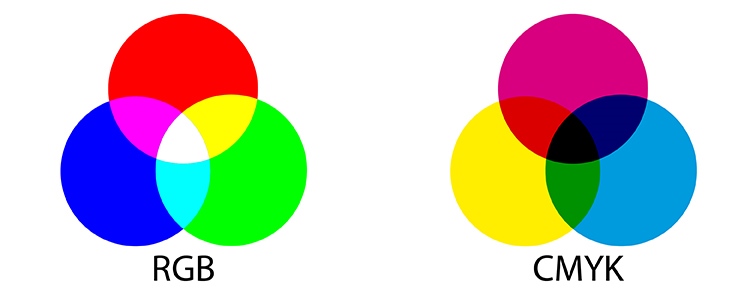
All colours within a colour model are assigned unique numerical values that can be read and interpreted by display devices such as monitor or output devices such as printers.
Find out more: What are the differences between the RGB colour model and the CMYK colour model? When is which colour model used?
Colour space
A colour space is the practical application and implementation of a colour model and its colours. Different colour spaces can exist within a colour model. Each defines a specific range of colours that can be created using a specific colour model. Within the RGB model there are, for example, the colour spaces sRGB and Adobe RGB, which have a different colour range.

Image: © The original uploader was Cpesacreta at English Wikipedia. / CC BY, edited by Br24
Display and output devices also have their own colour space within a colour model. For this reason, the display of colours differs depending on the device. The colours of a digital image look different on a monitor than on a printout.
Colour profile
The terms colour space and colour profile are often used interchangeably, because both describe the colour gamut of a reproduction medium. While a colour space is more like an overall standard, a colour profile refers to a specific reproduction medium and describes the individual colour space of a device. This can be a specific monitor, a specific printer or even a specific type of paper. Each reproduction medium has an individual colour space that varies from device to device and even between two devices of the same type.
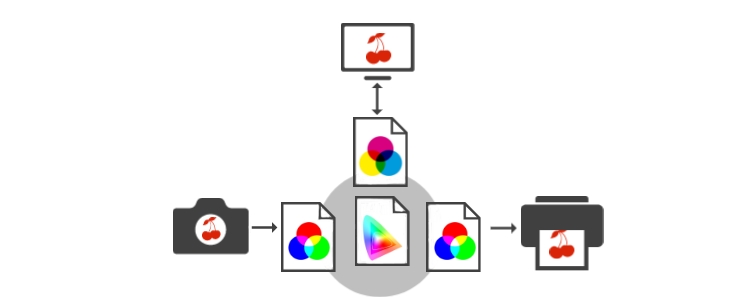
Using a colour profile, operating systems and programs can correctly interpret the colour values. For precise colour management, it is important that image files have an embedded colour profile.
Gamut mapping
The colour range, i.e. the range of colours that can be generated, of a reproduction medium is called gamut. In order to be able to reproduce colours on or with different devices, it is necessary to convert colour spaces (colour separation). For example, digital images are often converted from RGB to CMYK for printing. Since RGB can display significantly more colours than CMYK, certain colours have to be replaced. Which can lead to significant colour deviations (colour shifts).
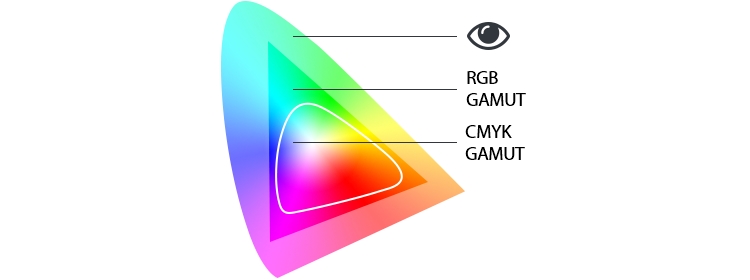
Image: © Ferlixwangg [CC BY-SA], edited by Br24
To keep colour deviations to a minimum when converting from one colour space to another, the non-reproducible colour values are replaced in such a way that the appearance of the colours and colour differences are retained as far as possible. This process of colour space adjustment is called gamut mapping.
- 2023
- January (1)
- 2022
- December (2)
- November (1)
- October (2)
- September (2)
- August (1)
- July (1)
- June (1)
- May (1)
- April (1)
- March (1)
- February (1)
- January (3)
- 2021
- December (2)
- November (1)
- October (3)
- September (2)
- August (1)
- July (3)
- June (1)
- May (2)
- April (1)
- March (1)
- February (2)
- January (4)
- 2020
- December (2)
- November (3)
- October (4)
- September (1)
- August (2)
- July (1)
- June (2)
- May (3)
- April (3)
- March (3)
- February (4)
- January (4)
- 2019
- December (1)
- November (2)
- October (5)
- September (1)
- August (3)
- July (2)
- June (2)
- May (3)
- April (2)
- March (3)
- February (2)
- January (4)
- 2018
- December (2)
- November (2)
- October (3)
- September (3)
- August (2)
- July (2)
- June (2)
- May (1)
- April (1)
- March (2)
- February (3)
- January (2)
- 2017
- December (2)
- November (2)
- October (1)
- September (1)
- August (1)
- July (1)
- June (1)
- May (1)
- April (1)
- March (1)
- February (1)
